How to Portforward a Minecraft Server Easy
Jul 26, 2022
Ignas R.
5min Read
How to Port Forward a Minecraft Server on Linux, Windows, and macOS

Creating your own Minecraft world on a local server can be exciting. However, it will only be visible to you, and playing alone can become tedious after a while. With the help of port forwarding, you can make a Minecraft server visible for anyone to connect and play.
This tutorial will show you how to port forward a server on Windows, macOS, and Linux and discuss the required configuration for this process.
Download Complete Linux Commands Cheat Sheet
What Is Port Forwarding?
If a user has a game server running locally on their machine and wants to play together with friends, connecting via an internal IP address, like 192.168.0.1, won't work as it is a local IP address.
Port forwarding allows remote computers to connect your router and local network by using specific TCP and UDP ports. Usually, the port forwarding feature is available on most routers and can be accessed by logging in via the default router gateway.
How to Port Forward Minecraft?
To make a Minecraft server visible publicly, you will need to find the default server port, allow it through a firewall, and tinker with your router configuration.
Step 1. Set the Port on Minecraft Configuration
- Open the Minecraft server directory and locate the server.properties file:
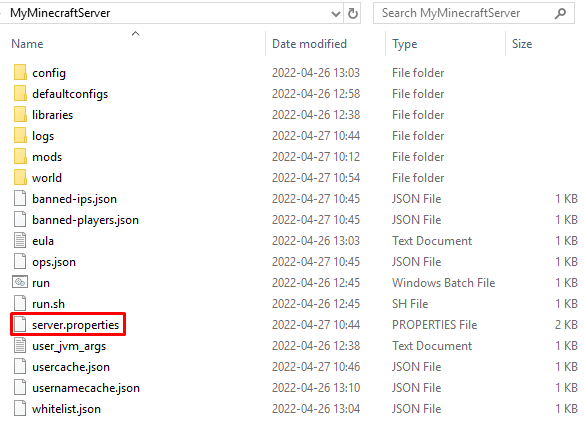
- Right-click on it and open the file with a text editor.
- Find the server-port line:
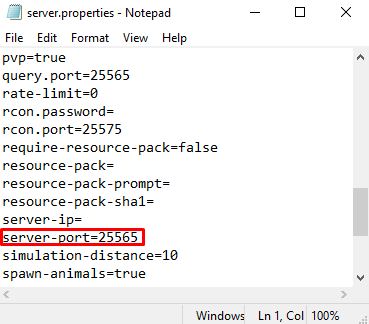
Here are the default port numbers for Minecraft:
- 25565 – for Java Edition.
- 19132-19133 – TCP and UDP ports for Bedrock.
Users can change the port by changing the server-port value to any in the range from 1 to 65535, although we recommend sticking with the default one.
Step 2. Allow the Port on Your Firewall
To ensure that the server works correctly, you will need to allow the Minecraft port number via your firewall. In this section, we will go over the process on three operating systems – Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Firewall Management on Windows
- Open Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security.
- Click on Inbound Rules and select New Rule.
- Choose Port and click Next.
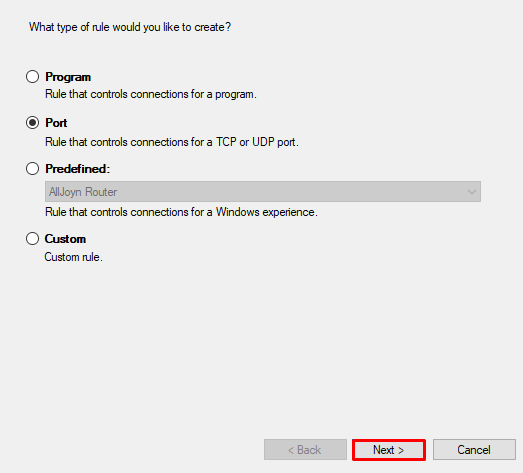
- Select TCP, and enter the Minecraft port number. In this case, it's 25565. Once done, click Next.
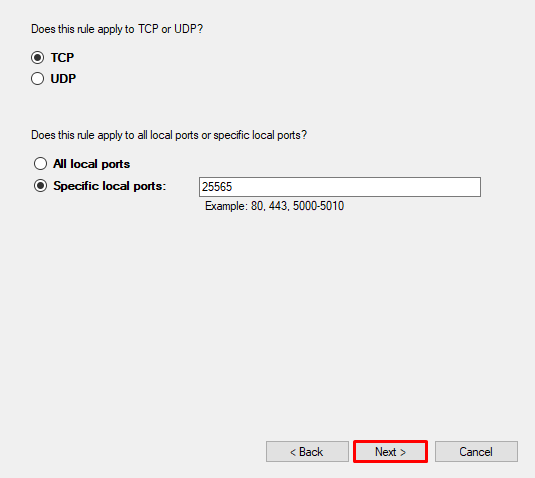
- Select Allow connection and click the Next button until the final step. Before clicking Finish, give your rule a name, like in this example:
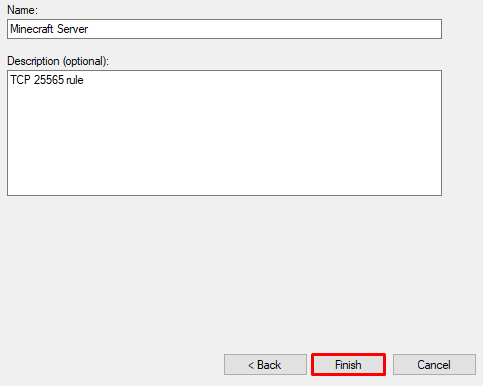
- After you have created the rule, make a new one with the same configuration, just for UDP.
Firewall Management on macOS
- Go to System Preferences and select Security & Privacy.

- Choose Firewall and click on the Firewall Options button.
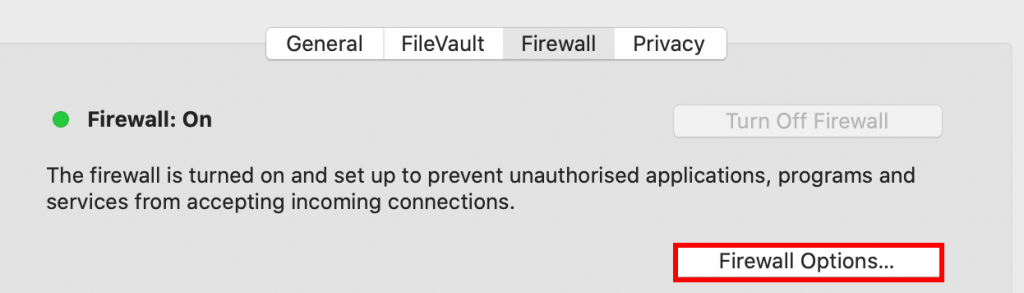
If the option is grayed out, select the lock icon on the lower-left corner to unlock Firewall Options.
- Click Add, find the installed Java application, and confirm the selection. Make sure that the Allow incoming connections option is checked.
Firewall Management on Linux
Unlike Windows or Mac, Linux comes with a more complex firewall. We recommend checking out our tutorial on how to configure your Ubuntu firewall.
Step 3. Forward the Port on the Router
With the firewall set up and incoming network requests allowed, proceed to create a port forward rule on your router. Even though each router has a different interface, the steps will be similar.
- Find your default gateway IP address. It will be used to log in to the router.
- Set up a static IP address.
- Open the port forwarding settings.
- Specify which TCP and UDP ports to forward.
Finding the Router Address and Setting up a Static IP on Windows
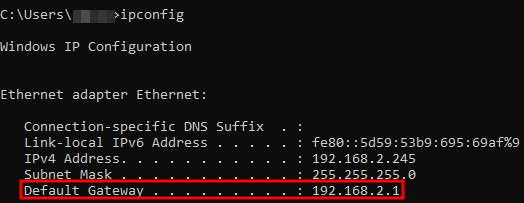
Press Windows + R and enter CMD to open the command prompt. Run the following command:
ipconfig
The router's IP address will be shown on the Default gateway line.
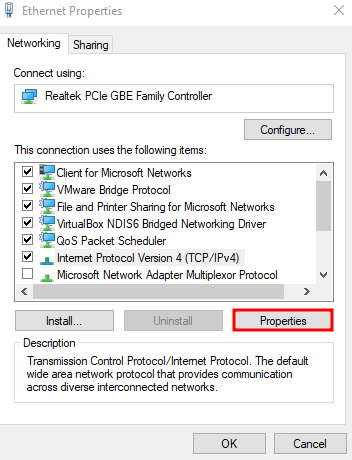
To set up a static IP address, press Windows + R again and enter ncpa.cpl. Right-click your network interface, select Properties, locate Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IP), and select Properties again:
Specify the preferred static IP address, subnet mask (255.255.255.0), and the router IP you acquired earlier.
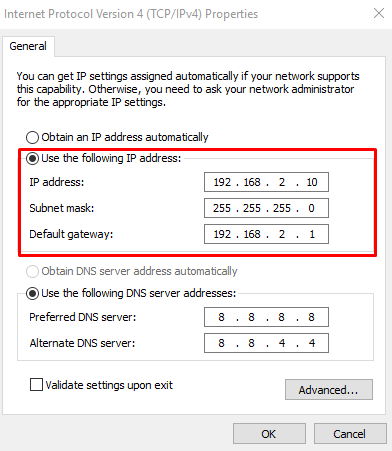
Once done, click OK to save the changes.
Finding the Router Address and Setting up a Static IP on macOS
- Go to System Preferences and select Network.
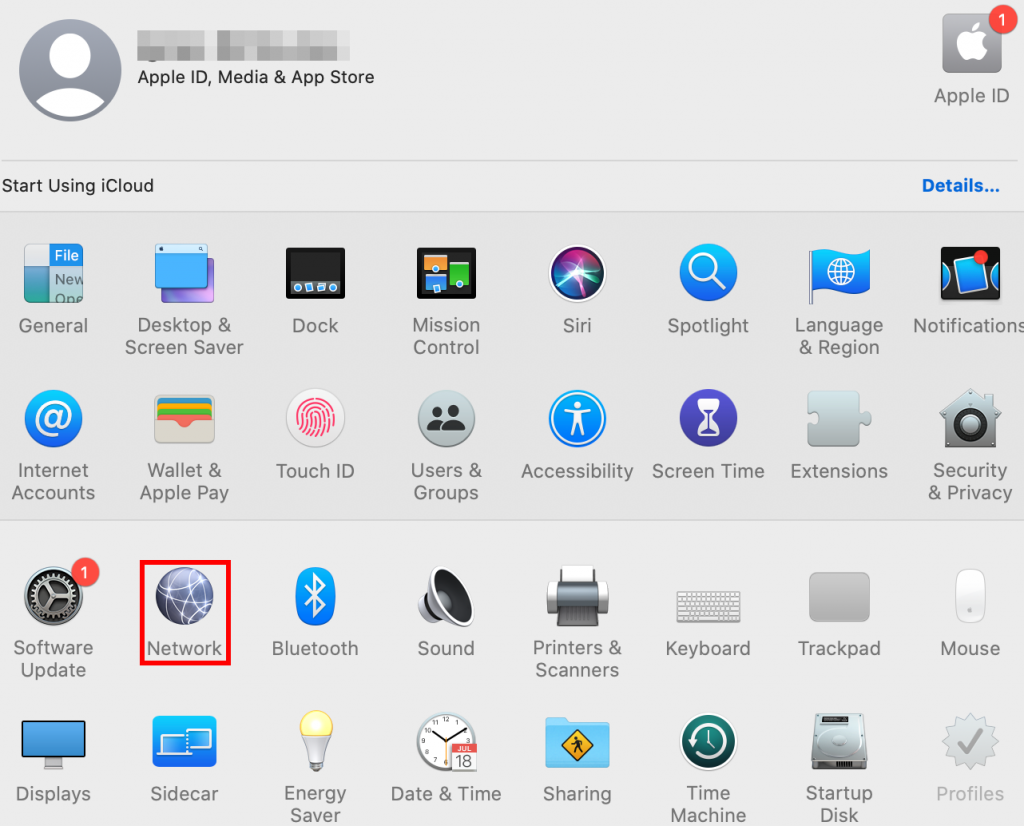
- Find the network you're using and click Advanced.
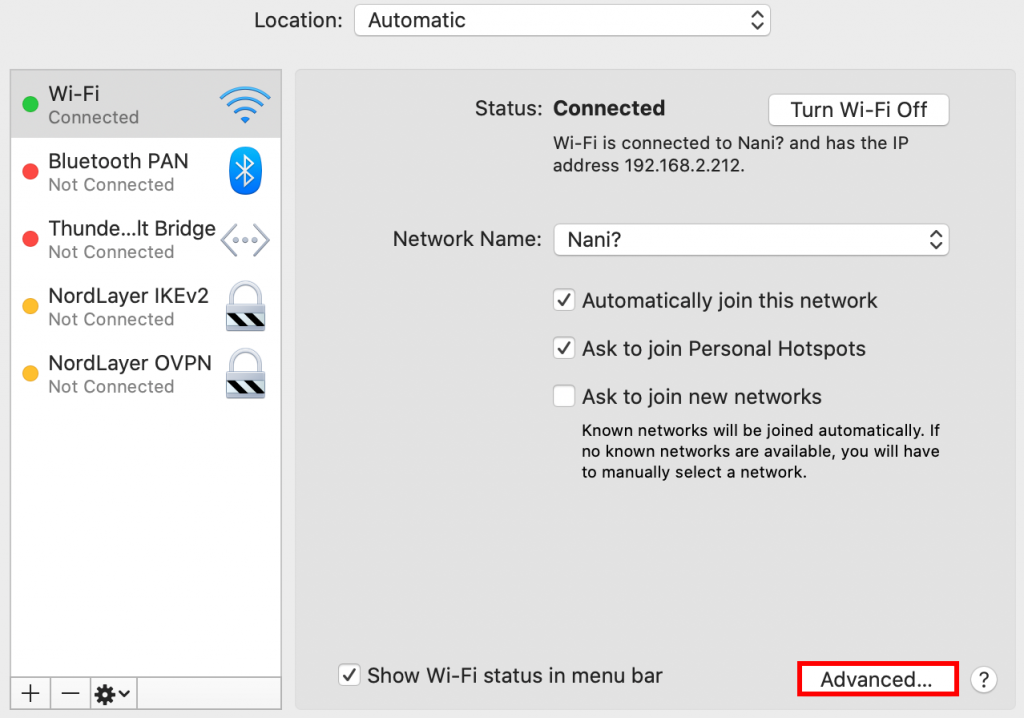
- Navigate to the TCP/IP tab. The Router line will contain the router's IP address.
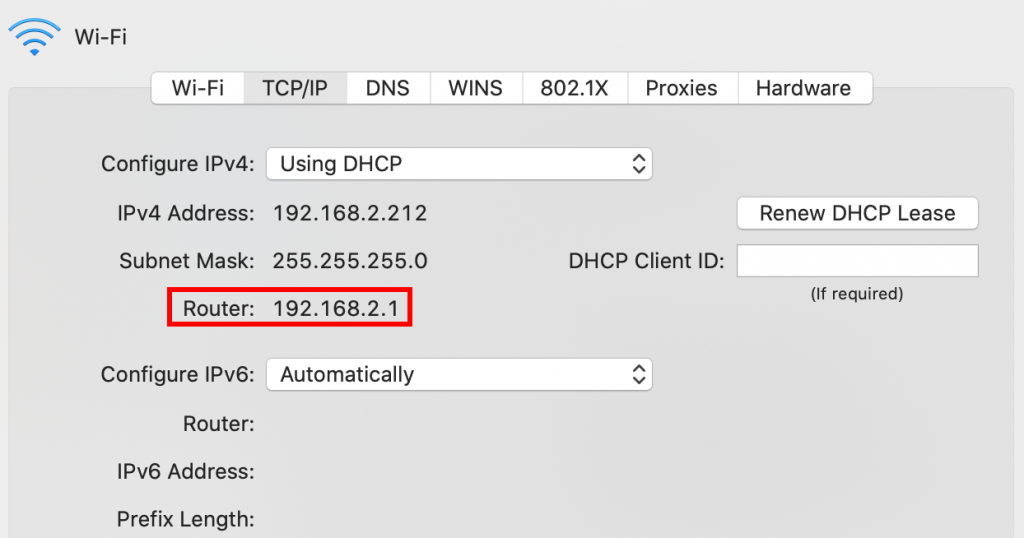
Alternatively, open Terminal and use the following command to check the router IP address:
netstat -nr|grep default
To set up a static local IP address, go back to the TCP/IP section, choose Using DHCP with manual address, and specify the IP you would like to use. We recommend adding a zero to the router IP.
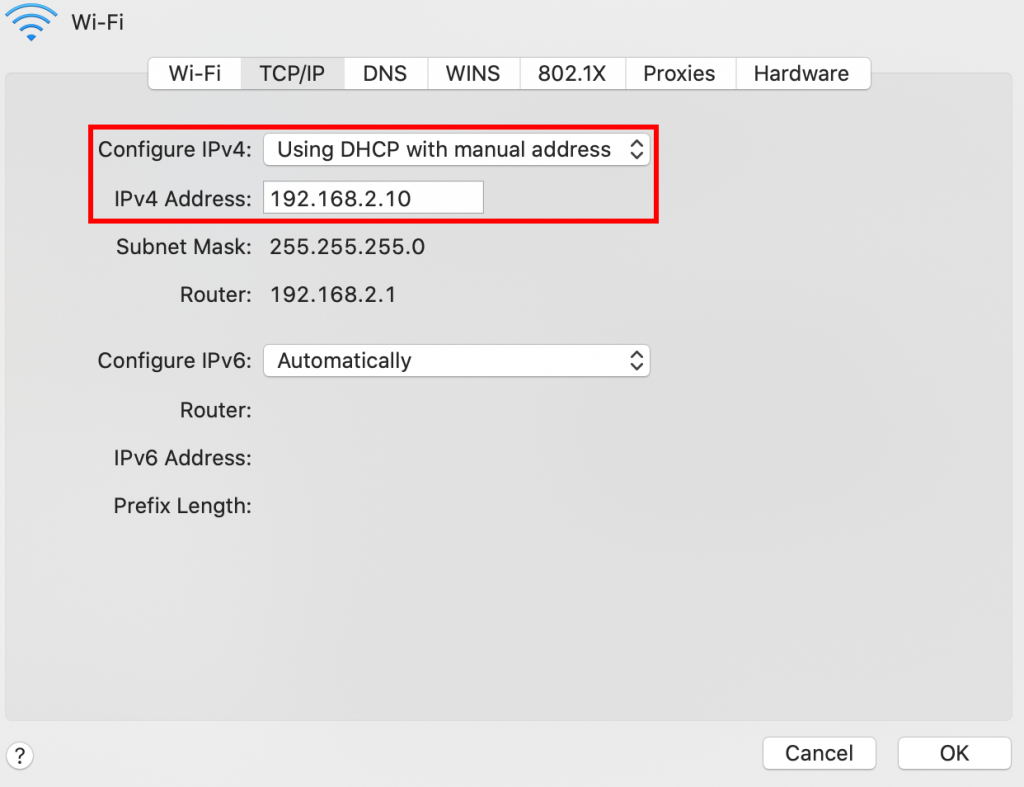
Click OK to save the changes.
Finding the Router Address and Setting up a Static IP on Linux
To check the router IP on Linux based systems, open Terminal and enter the following command:
route -n | grep "^0.0.0.0" | cut -d ' ' -f 10
To set up a static IP, you will need to edit the primary network configuration file. For example, the Ubuntu 18.04 configuration can be accessed by pasting this command into Terminal and pressing Enter:
sudo nano /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
Here's an example configuration where gateway4 is your router IP and addresses refers to your preferred static IPv4 address:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system # For more information, see netplan(5). network: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: ens33: dhcp4: no dhcp6: no addresses: [192.168.2.10/24] gateway4: 192.168.2.1 nameservers: addresses: [1.1.1.1,1.0.0.1]
Once done, save the changes made to the 01-netcfg.yaml file.
Logging in to the Router
Paste the router IP address into your browser's address bar and press Enter. A login page will appear.
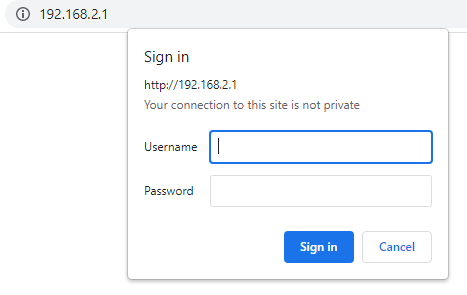
It will ask for a username and password. If you are unsure where to find them, check the stickers on your router. Another option is to Google the router's name and model number along with keywords like default login credentials.
Expert Tip
If your router is still using the factory default credentials, change them immediately as anyone could access your network.
Once logged in, look for options related to virtual server or port forwarding. In this tutorial, we'll use a D-Link router. Its interface for port forwarding looks like this:
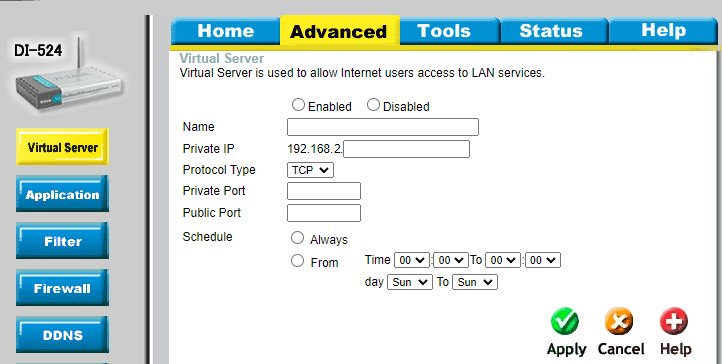
Check the Enabled option, give the forwarding rule a name, specify the local static IP address you've set previously, and enter the Minecraft server port. In this case, it's 25565.
Don't forget to apply the configuration for both TCP and UDP ports.
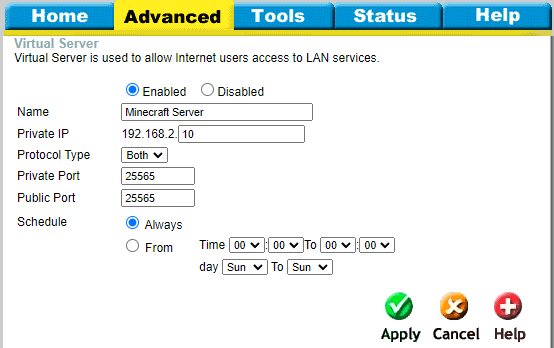
Once done, save the changes.
Pro Tip
If you are still unsure about the exact port forwarding procedure for your specific router, you can always Google the device name and look up the router's manual.
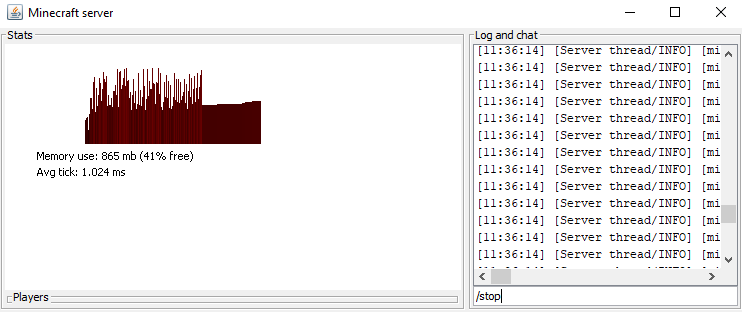
Step 4. Restart the Minecraft Server and Connect
For the port forwarding changes to apply, you will need to restart your Minecraft server. To do so, enter /stop on the server console and reinitialize the server.
Once the server has restarted, open Google and enter "What's my IP". This will show your public IP address that you will need to share with the people you want to play with.
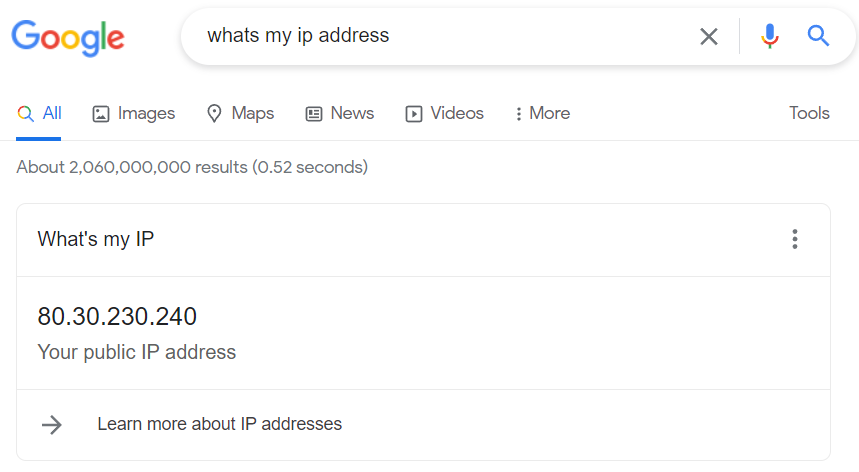
Expert Tip
Never share your public IP on the internet as this can expose your physical location and make you a target of cyber attacks.
Now players will be able to join the server. Keep in mind that if the default server port 25565 was changed, users would need to connect using the 185.185.185.185:port syntax.
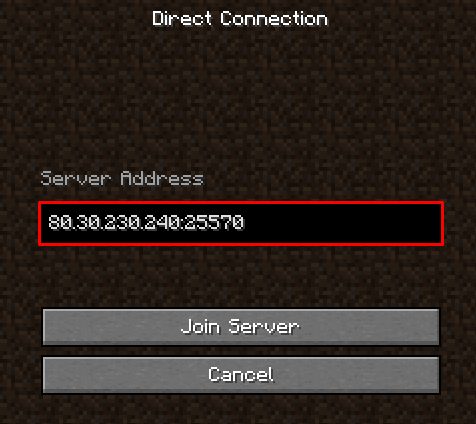
Alternatively, just enter the IP address.
Conclusion
Having a local Minecraft server with port forwarding allows you to play with other people, making your gameplay experience more exciting and unique.
In this tutorial, we have covered the process of port forwarding a Minecraft server on Windows, macOS, and Linux systems. We've also shown how to allow an application through a firewall and navigate the router interface.
Should you have any questions, feel free to leave them in the comments section below.
Source: https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/how-to-port-forward-a-minecraft-server


0 Response to "How to Portforward a Minecraft Server Easy"
Post a Comment